Frequently asked programming interview questions (with answers) and puzzles asked by google, microsoft, amazon, yahoo, and facebook for SDE/Developer and SDET positions.
Dynamic Programming Questions
1. Longest Common Subsequence http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_common_subsequence_problem
2.longest common substring problem http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_common_substring_problem
Object Oriented Programmings OOPS Concepts
Explain polymorphism with examples
What are the 4 basics of OOP?
Define Data Abstraction. What is its importance?
Design Questions
Design a class library for writing card games.
Design an elevator control system. Buttons are present on every floor and supporting multiple elevators. (What objects/methods/properties/how components communicate)
How would you design the infrastructure front half of a very large web ecommerce site? what if it was very personalized? (how sessions are handled? where and what you can cache? how to load-balance?)
Design a chess game
Design malloc() and free(). http://g.oswego.edu/dl/html/malloc.html
Questions
Array
String
Matrix
Linked List
Trees
Sorting
Sets
Numbers
Data Structures
Personal
- How would you detect a repeated element in an integer array?
- Design an algorithm and write code to find two numbers in an array whose sum equals a given value.
- Given an array of size N in which every number is between 1 and N, determine if there are any duplicates in it. You are allowed to destroy the array if you like.
- Given an array containing both positive and negative integers and required to find the sub-array with the largest sum in O(N)
- Given an array [100] which contains numbers between 1..99. Find the duplicate value.
- Write a function to find the K biggest elements in the array, and return the sum. Do both in O(n) time.
- Given an array A[string], an array of strings where each string represents a word in a text document. Also given 3 search terms T1, T2, and T3 and 3 corresponding sorted sequences of integers S1, S2, and S3 where each integer in Si represents an index in A where search term Ti occured (i.e. S1, S2, and S3 contain the locations of the search terms in our array of words). Now find a minimal subarray of A that contains all of the search terms T1, T2, and T3. Extend this algorithm for an arbitrary number of search terms.
- A “rotated array” is an array of integers in ascending order, after which for every element i, it has been moved to element (i + n) mod sizeOfList. Write a function that takes a rotated array and, in less-than-linear time, returns n (the amount of rotation).
- Find an Item in a Sorted Array with Shifted Elements
- Rotate/Shift an array: Given a char array and n (number by which to shift), the array characters had to be circular shifted by n . For example ABCDEF becomes DEFABC
- design a technique to initialize an entry of a vector to zero the first time it is accessed.
- Problem: Write code for implementing 2 stacks in 1 array *
- You’re given an array which contains the numbers from 1 to n, in random order, except there is one missing. Write a function to return the missing number.
- Write code to sort an array. Why did you chose your method? What are its pros and cons?
- Write a program to copy strings A and B. Last 10 characters of A overlap the first 10 characring B.
- Given an array of integers. The sum of the elements of the array is known to be less than the max integer. Compute the sum. What if we know that integers are in 2's complement form?
- Write code for extracting unique elements from a sorted list of array
- Given array of 1001 integers. All the integers are between 1 and 1000 (inclusive). Also, each integer can appear only once in the array except for one which occurs twice. Give an algorithm to find the repeated number. Assume that you can access each element of the array only once and try to solve it without using extra storage.
- Given two fixed length buffers padded with nulls/ Swap and reverse them, not swapping and reversing nulls.
- Write a program to compact an array (remove duplicates).
- Write a program to merge two arrays while removing duplicate elements
- Write a program to merge two sorted arrays. First array has extra space at the end to accommodate the second array.
- Array: Find the number with odd number of occurrences
- Function to perform Binary Search on a Sorted Array
- array of random numbers. Find the duplicate numbers.o(sqr(n)), O(nlogn), O(n)
- the first n cells of an array contain integers sorted in increasing order. The remaining cells all contain some very large integer tht we may think of as MAXINT. The array is arbitarily large (you may thnk infinite) and you donot know n. Give an algorithm to find the position of a given integer x (x < MAXINT) in the array. What is worst case running time of your algorithm ? Make your algorithm efficient. (Hint the problem can be solved in log n) time.
String
- You are given a C string. Design a function to remove duplicate characters. i.e. "aaabbbccc" → "abc", "abc abc abc" → "abc"
- Problem: Given an array of strings (char * a[100]). Each string is a word from the dictionary. Devise a way to determine and display all of the anagrams in the array. *
- Given two strings return a string that consists of intersection of the characters in the two strings
- Implement an algorithm to do string matching with wildcards
- Reverse a string in place *
- Reverse words in a sentence *
- Find a substring.
- Implement strstr() (or some other string library function).
- String compare
- Given a set of pointers to very long strings. Find the pointer to the lexicographically smallest and largest strings.
- Given strings A and B, delete from B all characters present in A.
- Implement strpbak
- Given a set of strings, write code to print the strings that are anagrams.
- Write a program to find acronyms ("Interview Question" becomes "I.Q.")
- String: Permutations Using Recursion *
- Convert Integer to String itoa *
- Convert String To Integer atoi *
- Find First Non-Repeated Character *
- String: Palindrome Check *
- Write a function to count the number of characters, number of words in a paragraph
- Given a sequence of characters. How will you convert the lower case characters to upper case characters. ( Try using bit vector solutions given in the C lib -typec.h)
Matrix
- Given an NxN matrix of positive and negative integers. Write some code that finds the sub-matrix with the maximum sum of its elements.
- Write code to print a 2 dimensional matrix in spiral sequence
- What is the time complexity of matrix multiplication ?
Linked List
- Implement a linked list
- You are given a list of numbers. When you reach the end of the list you will come back to the beginning of the list (a circular list). Write the most efficient algorithm to find the minimum # in this list. Find any given # in the list. The numbers in the list are always increasing but you don’t know where the circular list begins, ie: 38, 40, 55, 89, 6, 13, 20, 23, 36.
- Sort a linked list in. Can you do it in O(n)?
- Write code for reversing a doubly linked list
- Reverse a singly linked list using recurssion and iteration
- Given a linked list find the center of the linked list. *
- Get the data stored in the nth position of a linked list
- Pop for linked list
- Count the number of times a given number occurs in a linked list.
- Insert a new node at nth index
- SortedInsert in a linked list
- Sort a linked list. It should use SortedInsert method from above question
- Append on linked list to another
- Given a linked list, split it into two lists one for the front half and, one for the last half. If odd number of elements are present the extra node should go to the front list
- Remove duplicates from a linked list
- Write a function to divide the nodes in a lists in an alternate fashion
- Merge Sort a list using FrontBackSplit and SortedMerge
- SortedMerge takes two sorted lists and merges them.
- SortedIntersect: Given two sorted linked lists, create and return a new linked list that represents the intersection of the two.
- Reverse and recursive reverse a linked list *
- Write code to reverse a linked list.
- Write a program to insert a new node in a circular linked list without traversing it.
- Find nth element in the linked list from back
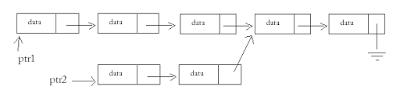
- Merged List Problem
- Given are 2 singly linked lists (list1 and list2) that merge at one of the nodes and share the nodes there onwards. The goal is to find the node where these linked lists merge or join.
- Given a singly linked list, determine whether it contains a loop or not.
- Under what circumstances can one delete an element from a singly linked list in constant time?
Trees
- Write a program that performs a breadth first traversal of a binary tree.*
- Write a program that finds the depth of a binary tree.
- You must serialize and deserialize a binary tree. Design two functions such that: char *f(Node *); Node *g(char *); tree = g(f(tree);
- Write a function to reconstruct a binary tree from its preorder traversal and inorder traversal. Take into account that the traversals could be invalid.
- You are given two nodes in a tree. Write a program to find the common root of the nodes. *
- How do you represent an n-ary tree. Write a program to perform an breadth first traversal of this n-ary tree.
- What is a balanced tree?
- Print data in a binary tree, level by level, starting at the top. Breath First Traversal/Search. *
- Write code to traverse a binary tree and set the parent node for all the nodes.
- Given a binary tree with nodes, print out the values in pre-order/in-order/post-order without using any extra space.
- How do you traverse a Btree in Backward in-order?
- Process the node in the right subtree
- Process the root
- Process the node in the left subtree
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of B-star trees over Binary trees?
Sorting
- How to implement a Merge Sort on disk
- How to sort 10 million 7 digit unique phone numbers with ~ 1 MB memory?
- Implement quick sort
- Compare and contrast the sorting algorithms you know
Sets
- Given two sets, Write a function to provide the union of them.
- Given a fixed list of numbers A. compare with another list B to find out if an element in A exists in B
Numbers
- Given a number, describe an algorithm to find the next number which is prime.
- Write a program to print the Fibonacci sequence.
- Convert a decimal number to a roman numeral given a set of numerals
Data Structures
- Propose a good data structure that can hold 'n' queues in a finite memory segment. you are allowed to have some datastructure separate for each queue.Try to consume at least 90% of the memory space.
- Implement a trie (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie) data structure. Write a function add, which takes a word, and a trie, and adds the word to the trie. Write another function lookup, which takes a prefix and a trie, and returns all the words in the trie that start with that prefix.
- Difference between a linked list and an array
- Write a function to manage a heap using an existing array
- How do you optimize symbol table storage
- Write a hashing function for a hashtable that can contain 1 million rows.
- Implement a queue using 2 stacks
- Implement a Queue using an Array
- What's the big-O for growing a vector?
- Describe one simple rehashing policy.(Asked by Motorola people)
- Describe Stacks and name a couple of places where stacks are useful. (Asked by Microsoft)
- What is the major advantage of a hash table? (Asked by Silicon Magic Corp. people)
- What are the techniques that you use to handle the collisions in hash tables?(Asked by Silicon Magic Corp. people)
- What is a virtual function in C++
- What is a default constructor?
- What is a conversion constructor?
- What is a copy constructor?
- What is an explicit constructor?
- What is the difference between a copy constructor and an overloaded assignment operator?
- what happens if there is an error in constructor destructor?
- What is the difference between an abstract class and an interface?
- What is the difference between malloc(), calloc(), and realloc()? *
- What are the advantages of OOPL?
- Basic concepts, like is-a vs. has-a (with examples), overloading vs. overriding, class vs. object, method vs. function, virtual vs.pure virtual, base class vs. derived class, inheritance, encapsulation, delegation, aggregation
- What's the difference between pointers and references in C++?
- What's a static variable?
- What's the heap?
- What's the difference between call-by-reference and call-by-value?
- Do they understand the scope of variables and how the stack is used?
- What is polymorphism?
- Why is polymorphism better than simple collection of source files with subroutines and data structures?
- What's a virtual function and how do they work?
- When should you use multiple inheritance?
- What is a virtual destructor?
- What is a mutable member?
- c++: Describe run-time type identification.
- What problem does the namespace feature solve?
- What is a Make file?
- In C++, what is the difference between method overloading and method overwriting?
- In the derived class, which data member of the base class are visible?
- Implement a thread-safe class that will read/write to/from a buffer
- Write an algorithm for Soduku puzzle
- Solve the mouse in a maze problem
- Wire Routing Problem using Queues.
- How could you generate a file of k unique random integers between 0 and n-1 in random order?
- Write a function to smooth out stock fluctuations.
- Write a small lexical analyzer. it should be able to parse simple expressions like a*b
- What is the solution to the reader-writers problem
- Implement a multiple-reader-single-writer lock given a compare-and-swap instruction. Readers cannot overtake waiting writers.
- Write an efficient algorithm and C code to shuffle a pack of cards. The cards are stored in an array of integers.
- Order the following runtimes in order of their asymptotic performance O(2^n), O(n^y), O( 10^100), O(n!), O(n^n)
- Implement malloc or write the code for malloc memory allocation function.
- Given a square with side length of 1 unit, describe all points inside square that are closer to the center of the square than to the edge of the square.
- You are given a list of Ball objects. Each Ball is either Red or Blue. Write a function that partitions these balls so that all of the balls of each color are contiguous. Return the index of the first ball of the second color (your result can be Red balls, then Blue balls, or the other way around). In haskell, you’ll probably want to return a ([Ball],Int).
- Live Search is a search engine. Suppose it was to be tied into an online store. Now you’re given two lists. One is a [(SessionId, NormalizedQuery)]. That is, when a particular user performs a query, it is turned into some consistent format, based on their apparent intent, and stored in this logfile. The second list is a [(SessionId, ProductId)]. This indicates the product bought by a particular user. Now, you want to take these two (potentially very long) lists, and return some structure that will make it easy to take a query and return a list of the most popular resulting purchases. That is, of people who have run this query in the past, what are the most common products they’ve wound up buying? The interviewer said that this is an instance of a well-known problem, but I didn’t catch the name of it.
- You have a [(WeatherStationId, Latitude, Longitude)]. Similar to #3, write a function which will, off-line, turn this into a data structure from which you can easily determine the nearest Weather Station, given an arbitrary Latitude and Longitude.
- Write a function for scoring a mastermind guess. That is, in a game of mastermind (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mastermind_(board_game)), given a guess, and the actual answer, determine the number correct, the number wrong,and the number out of place.
- Write an algorithm to shuffle a deck of cards. Now write a function to perform some kind of evaluation of “how shuffled” a deck of cards is.
- Space-time trade off: You are given a 5x5 grid where each cell has a weight associated to it, and a scale with the ability to give the total weight of any arbitrary selection of cells. In this grid, four of the five rows contain only one pound weights. One of the five rows contains only two pound weights. What is the minimum number of times you must use the scale, and in what configuration, to find the row with the two pound weights.
- Write code to read and write from a bounded buffer
- Function to select the eight strongest radio stations in a radio
- Design and implement a self managing Thread Pool class
- Write a function to draw a circle. (x**2 + y**2 = r** 2). You cannot use any floating point computations.
- Write a routine putlong() that prints out an unsigned long in decimal numbering system. You are allowed to use only putchar (no sprintf, itoa, etc)
- In the game of tic tac toe, write a program to generate moves by a computer. This should be fast.
- How would you go about finding out where to find a book in a library ( You dont know before hand how exactly the books are organized).
- Given a tree control in a Windows User Interface. How would you read information from a database and display it in the tree control. The tree has arbitrary levels and each level can contain arbitrary number of items in it.
- DNA Sequence Pattern Match/ String Search Problem
- Given a stream of numbers, suggest a data structure to store the numbers in the stream along with their number of occurrences.
- Write a function that adds 30 days to a given date.
- How would you design a restaurant reservation system, parking lot, elevator, vending machine (gen question). (test an elevator, vending machine, online shopping cart)
- Find the angle of a clock at a particular time
- You, a designer want to measure disk traffic i.e. get a histogram showing the relative frequency of I/O/second for each disk block. The buffer pool has b buffers and uses LRU replacement policy. The disk block size and buffer pool block sizes are the same. You are given a routine int lru_block_in_position (int i) which returns the block_id of the block in the i-th position in the list of blocks managed by LRU. Assume position 0 is the hottest. You can repeatedly call this routine. How would you get the histogram you desire?
- Write a function to check if two rectangles defined as below overlap or not. struct rect { int top, bot, left, right; } r1, r2;
- Write a SetPixel(x, y) function, given a pointer to the bitmap. Each pixel is represented by 1 bit. There are 640 pixels per row. In each byte, while the bits are numbered right to left, pixels are numbered left to right. Avoid multiplications and divisions to improve performance.
- A character set has 1 and 2 byte characters. One byte characters have 0 as the first bit. You just keep accumulating the characters in a buffer. Suppose at some point the user types a backspace, how can you remove the character efficiently. (Note: You cant store the last character typed because the user can type in arbitrarily many backspaces)
- Write the 'tr' program of UNIX. Invoked as tr -str1 -str2. It reads stdin and prints it out to stdout, replacing every occurance of str1[i] with str2[i].
- First some definitions for this problem: a) An ASCII character is one byte long and the most significant bit in the byte is always '0'. b) A Kanji character is two bytes long. The only characteristic of a Kanji character is that in its first byte the most significant bit is '1'. Now you are given an array of a characters (both ASCII and Kanji) and, an index into the array. The index points to the start of some character. Now you need to write a function to do a backspace (i.e. delete the character before the given index).
- Write a program to find if a machine is big-endian or little-endian.
- How do you test if a number if power of 2.
- Write a function to figure out if a computer's stack grows up or down.
- How can you align a pointer to a 4 byte boundary in an efficient way.
- How do you find if the sum of two unsigned integers has resulted in an overflow?
- reverse all the bits in the byte
- count the number of set bits in a number. Optimize for speed and time.
- multiply a number by 8 without using the * or + operators. Can you multiply with 7?
- Add numbers in base n (not any of 10,16,8, or 2) -2 charles simonyi
- Exchange two numbers without using a temporary say a = 8 and b = 10
- a = a+b b = a-b a = a-b
- array of 0's and 1's. Give an efficient algorithm to count the number of 0's and 1's
- What are the logical operations? (AND, OR, NOT, XOR.)
- What's the difference between logical-AND and bitwise-AND?
- What is 36 expressed in hexadecimal?
- Write an if-statement that tests whether the high order bit is set in a byte.
- Reverse the bits of an unsigned integer.
- Compute the number of ones in an unsigned integer.
- Compute the discrete log of an unsigned integer.
- How do we test most simply if an unsigned integer is a power of two?
- Set the highest significant bit of an unsigned integer to zero.
- Let f(k) = y where k is the y-th number in the increasing sequence of non-negative integers with the same number of ones in its binary representation as y, e.g. f(0) = 1, f(1) = 1, f(2) = 2, f(3) = 1, f(4) = 3, f(5) = 2, f(6) = 3 and so on. Given k >= 0, compute f(k).
- What is a volatile variable?
- What is a deadlock?
- What is a Semaphore?
- How does the race condition occur?
- What are mutex and semaphore? What is the difference between them?
- What are the disadvantages of using threads?
- Describe synchronization in respect to multithreading.
- What is Virtual Memory?
- What is multiprogramming?
- Assuming that locks are the only reason due to which deadlocks can occur in a system. What would be a foolproof method of avoiding deadlocks in the system.
- What is Boyce Codd Normal form?
- Write a query to find the zip codes for all the orders within the last 24 hours. (to see if one can write basic queries to join 2 tables)
- Write a SQL Query to find first day of month?
- Why there is a performance difference between two similar queries that uses UNION and UNION ALL?
- How to choose between a Clustered Index and a Non-Clustered Index?
- How you can minimize the deadlock situation?
- When you should use low fill factor?
- Explain Third normalization form with an example?
- What is a Cartesian product? What causes it?
- What is an advantage to using a stored procedure as opposed to passing an SQL query from an application.
- What is the difference of a LEFT JOIN and an INNER JOIN statement?
- When a query is sent to the database and an index is not being used, what type of execution is taking place?
- What are the pros and cons of using triggers?
- What are the pros and cons of using stored procedures. When would you use them?
- What are the pros and cons of using cursors? When would you use them?
- What is the difference between TCP and UDP?
- How do you use RSA for both authentication and secrecy?
- What is ARP and how does it work?
- What's the difference between a switch and a router?
- Name of seven layers in Open System Interconnection model.
- Name some routing protocols? (RIP,OSPF etc..)
- Give 4 examples which belongs application layer in TCP/IP architecture? (from CISCO )
- How do you do authentication with message digest(MD5)? (Usually MD is used for finding tampering of data)
- How do you implement a packet filter that distinguishes following cases and selects first case and rejects second case.
- i) A host inside the corporate n/w makes a ftp request to outside host and the outside host sends reply.
- ii) A host outside the network sends a ftp request to host inside. for the packet filter in
- both cases the source and destination feilds will look the same.
- How does traceroute works? Now how does traceroute makes sure that the packet follows the same path that a previous (with ttl 1) probe packet went in?
- Explain Kerberos Protocol?
- What are digital signatures and smart cards?
- Difference between discretionary access control and mandatory access control?
- What is the goal of the shortest distance algorithm ?
Personal
- Tell me the courses you liked and why did you like them.
- Give an instance in your life in which u were faced with a problem and you tackled it successfully
- What is your ideal working environment. ( They usually to hear that u can work in group also.)
- Why do u think u are smart.
- Questions on the projects listed on the Resume.
- Do you want to know any thing about the company.( Try to ask some relevant and interesting questions)
- How long do u want to stay in USA and why?
- What are your geographical preference?
- What are your expectations from the job.
- Suppose a 3-bit sequence number is used in the selective-reject ARQ, what is the maximum number of frames that could be transmitted at a time? (Asked by Cisco) A5 If a 3-bit sequence number is used, then it could distinguish 8 different frames. Since the number of frames that could be transmitted at a time is no greater half the numner of frames that could be distinguished by the sequence number, so at most 4 frames can be transmitted at a time.
- Trade off between time spent in testing a product and getting into the market first.
- What to test for given that there isn't enough time to test everything you want to.
- Fly plane around the world half fuel puzzle *
- Classic: If a bear walks one mile south, turns left and walks one mile to the east and then turns left again and walks one mile north and arrives at its original position, what is the color of the bear. ANS. The color of the bear is trivial. The possible solutions to it are interesting. In addition to the trivial north pole and circle near north pole solutions, there is an additional circle near south pole solution. Think it out.
- Given a rectangular (cuboidal for the puritans) cake with a rectangular piece removed (any size or orientation), how would you cut the remainder of the cake into two equal halves with one straight cut of a knife? ANS. Join the centers of the original and the removed rectangle. It works for cuboids too!
- There are 3 baskets. one of them have apples, one has oranges only and the other has mixture of apples and oranges. The labels on their baskets always lie. (i.e. if the label says oranges, you are sure that it doesn't have oranges only,it could be a mixture) The task is to pick one basket and pick only one fruit from it and then correctly label all the three baskets. HINT. There are only two combinations of distributions in which ALL the baskets have wrong labels. By picking a fruit from the one labeled MIXTURE, it is possible to tell what the other two baskets have.
- You have 8 balls. One of them is defective and weighs less than others. You have a balance to measure balls against each other. In 2 weighings how do you find the defective one?
- Why is a manhole cover round?
- How many cars are there in the USA? (A popular variant is "How many gas stations are there in the USA?")
- How many manhole covers are there in the USA?
- You've got someone working for you for seven days and a gold bar to pay them. The gold bar is segmented into seven connected pieces. You must give them a piece of gold at the end of every day. If you are only allowed to make two breaks in the gold bar, how do you pay your worker?
- One train leaves Los Angeles at 15mph heading for New York. Another train leaves from New York at 20mph heading for Los Angeles on the same track. If a bird, flying at 25mph, leaves from Los Angeles at the same time as the train and flies back and forth between the two trains until they collide, how far will the bird have traveled?
- Imagine a disk spinning like a record player turn table. Half of the disk is black and the other is white. Assume you have an unlimited number of color sensors. How many sensors would you have to place around the disk to determine the direction the disk is spinning? Where would they be placed?
- Imagine an analog clock set to 12 o'clock. Note that the hour and minute hands overlap. How many times each day do both the hour and minute hands overlap? How would you determine the exact times of the day that this occurs?
- You have two jars, 50 red marbles and 50 blue marbles. A jar will be picked at random, and then a marble will be picked from the jar. Placing all of the marbles in the jars, how can you maximize the chances of a red marble being picked? What are the exact odds of getting a red marble using your scheme?
- Pairs of primes separated by a single number are called prime pairs. Examples are 17 and 19. Prove that the number between a prime pair is always divisible by 6 (assuming both numbers in the pair are greater than 6). Now prove that there are no 'prime triples.'
- There is a room with a door (closed) and three light bulbs. Outside the room there are three switches, connected to the bulbs. You may manipulate the switches as you wish, but once you open the door you can't change them. Identify each switch with its bulb.
- Suppose you had 8 billiard balls, and one of them was slightly heavier, but the only way to tell was by putting it on a scale against another. What's the fewest number of times you'd have to use the scale to find the heavier ball?
- Imagine you are standing in front of a mirror, facing it. Raise your left hand. Raise your right hand. Look at your reflection. When you raise your left hand your reflection raises what appears to be his right hand. But when you tilt your head up, your reflection does too, and does not appear to tilt his/her head down. Why is it that the mirror appears to reverse left and right, but not up and down?
- You have 4 jars of pills. Each pill is a certain weight, except for contaminated pills contained in one jar, where each pill is weight + 1. How could you tell which jar had the contaminated pills in just one measurement? Try for 5 too.
- The SF Chronicle has a word game where all the letters are scrambled up and you have to figure out what the word is. Imagine that a scrambled word is 5 characters long: 1. How many possible solutions are there? 2. What if we know which 5 letters are being used? 3. Develop an algorithm to solve the word.
- There are 4 women who want to cross a bridge. They all begin on the same side. You have 17 minutes to get all of them across to the other side. It is night. There is one flashlight. A maximum of two people can cross at one time. Any party who crosses, either 1 or 2 people, must have the flashlight with them. The flashlight must be walked back and forth, it cannot be thrown, etc. Each woman walks at a different speed. A pair must walk together at the rate of the slower woman's pace. Woman 1: 1 minute to cross Woman 2: 2 minutes to cross Woman 3: 5 minutes to cross Woman 4: 10 minutes to cross For example if Woman 1 and Woman 4 walk across first, 10 minutes have elapsed when they get to the other side of the bridge. If Woman 4 then returns with the flashlight, a total of 20 minutes have passed and you have failed the mission. What is the order required to get all women across in 17 minutes? Now, what's the other way?
- If you had an infinite supply of water and a 5 quart and 3 quart pail, how would you measure exactly 4 quarts?
- You have a bucket of jelly beans. Some are red, some are blue, and some green. With your eyes closed, pick out 2 of a like color. How many do you have to grab to be sure you have 2 of the same?
- If you have two buckets, one with red paint and the other with blue paint, and you take one cup from the blue bucket and poor it into the red bucket. Then you take one cup from the red bucket and poor it into the blue bucket. Which bucket has the highest ratio between red and blue? Prove it mathematically.
- A version of the "There are three persons X Y Z, one of which always lies".. etc..
- There are 3 ants at 3 corners of a triangle, they randomly start moving towards another corner.. what is the probability that they don't collide.
- Which way should the key turn in a car door to unlock it?
- If you could remove any of the 50 states, which state would it be and why?
- There are four dogs/ants/people at four corners of a square of unit distance. At the same instant all of them start running with unit speed towards the person on their clockwise direction and will always run towards that target. How long does it take for them to meet and where? HINT. They will meet in the centre and the distance covered by them is independent of the path they actually take (a spiral).
- (from Tara Hovel) A helicopter drops two trains, each on a parachute, onto a straight infinite railway line. There is an undefined distance between the two trains. Each faces the same direction, and upon landing, the parachute attached to each train falls to the ground next to the train and detaches. Each train has a microchip that controls its motion. The chips are identical. There is no way for the trains to know where they are. You need to write the code in the chip to make the trains bump into each other. Each line of code takes a single clock cycle to execute. You can use the following commands (and only these); MF moves the train forward MB moves the train backward IF (P) conditional that's satisfied if the train is next to a parachute. There is no "then" to this IF statement.
- C#/.NET
- Reference/value type, stack vs heap, garbage collectpr
- boxing vs unboxing
- const vs readonly
- delegates vs events
- generics
- partial classes - what is and what problem is solved
- nullable types
- config relatinships: app.config, web.config, machine.config
- ASP.NET
- Controls and Pafe Life Cycle
- Order these in the correct order
- Static constructor
- class constructor
- PreInit
- Init
- InitComplete
- PreLoad
- Load
- LoadComplete
- Validation
- Event Handling
- PreRender
- PreRenderComplete
- Render
- Unload
- DataBinding (can happen anytime between Init and PreRender)
- State
- Compare these in terms of scope, life cyle, pros/cons
- Application (system.web.HttpApplicationState)
- Cache(system.web.Caching.Cache)
- Items (System.Web.httpContext.Items)
- Sessions (system.web.UI.HttpSessionState)
- Profile (System.Web/HttpContext.Profile) ASP.NET 2.0
- ViewState (system.Web.UI.COntrol.ViewState)
- ControlState (System.Web.UI.Control.ControlState) ASP.NET 2.0
- Cookies (System.Web.HttpRequest.Cookies)
- Query String Paramters (System.Web.HttpRequest.QueryString)
- Hidden Input Fields (System.Web.UI.ClientScriptManager.RegisterHiddenField(....))
- Page Intrinsics
- Discuss the purpose and usage of these:
- Request (System.Web.HttpRequest)
- Response
- Context System.Web.HttpContext
- Server System.Web.HttpServerUtility
- ClientScript System.Web.UI.CLientScriptManager
- Trace System.Web.TraceContext
- Browser System.Web.ttpBrowserCapabilities
- Controls
- Compare and contrast
- Server Controls (webControls, HtmlComtrols, Composite Controls, Custom Controls)
- Templates Controls (UserControls, Page)
- Web Parts - .NET 2.0 or Sharepoint 2.0
- Conceptual Questions
- Compare Server.Transfer(...) vs Request.Redirect(...)
- Describe how ASP.NET builds and renders pages
- How are master pages implemented
- How do you add javascript to an asp.net page
- IIS Administration
- AppPool vs Website vs Virtual Directory
- Posts or Host geaders for multiple roots
- XHTML 1.0/1.1
- Difference from HTML 4.01? How to get valid xhtml?
- Which browser classes should you code/test for?
- Describe building complex or columnar layouts without nested tables
- CSS 2.1
- Give syntax for each select and explain what each sleector matches
- Any element: "*"
- Class ".className"
- Element: "ElementName" e.g. "div"
- ID: "#ElementID" e.g. "#ctrl01_myDiv"
- PseudoClass "Selector:PseudoClass" e.g. "A:hover"
- Box model
- Draw a diagram of how each of these porperties exists within the box model: margin, padding, border, width, height, left, top
- Positioning
- Describe usage and values for "float"
- Describe usage and values for "position"
- contract methods for hiding elements
- Media Types
- Explain how to target a set of styles to a specific media type (e.g. printing with white background)
- Advanced Techniques
- Describe effects and usages of setting a negative margin on a block
- describe and discuss image replacement technique
- javascript
- What is the syntax for declaring variables?
- Contrast with C# or java
- Object oriented javascript
- descibr classes in javascript
- describe usage of prototype keyword
- DOM familiarity
- find an element via id
- find an element via tag
- show a message box
- ask the user for permission
- get input from the user
- XSLT
- Contrast xsl:stylesheet vs xsl:template
- what is match="..." in xsl:template
- calling templates vs applying templates
- Flow control?
- XPath expression
- XML in .NET
- Name some methods for generating xml in .NET
- XmlWriter
- XmlDocument
- Serialization
- DataSet.WriteXml()
- XpathDocument using external XSLT
- How do you control/customize serialization
- using serializable attribute
- Decorate class members with atributes to rename/ignore/specify types
- Implement ISerializable and manually control via another method
- Threading and Synchronization
- Mutex corss process
- sybc() {} for critical sections
- ReaderWriter lock
- Semaphores
- WebService
- C# attribute for decorating as webservice
- Webservices base class: what value if can decorate with attributes
- Design considerations vs. remoting or sharing libraries?
- Design patterns in .NET
- C# iterators
Labels:
Questions-List
Virtual Functions/Methods Runtime-Polymorphism
Question: Explain the significance of virtual methods and describe how they are invoked?
Virtual methods are used to support runtime polymorphism in object oriented languages.
Difference between an interface and an abstract class
Two most important differences are:
1. A class can implement several interfaces but can inherit from a single abstract class (or any class for that matter)
2. Interfaces do not contain any implementation while abstract classes can contain some default implementation of methods.
Function to perform Binary Search on a Sorted Array
Problem: Write a function to perform a binary search on a Sorted Array.
Solution: The recursive solution below runs in O(log(n)) because the problem size is halved with each recursive call.
Solution: The recursive solution below runs in O(log(n)) because the problem size is halved with each recursive call.
// returns the index of the target element if found, else returns -1
static int Binary_Search(int[] arr, int start, int end, int target)
{
int medianIndex = (end - start) /2 + start;
int medianValue = arr[medianIndex];
if(start == end && arr[start] != target)
return -1;
if (medianValue == target)
return medianIndex;
else if (medianValue < target)
return Binary_Search(arr, medianIndex + 1, end, target);
else
return Binary_Search(arr, start, medianIndex - 1, target);
}
Labels:
Array
Telephone Words Using Recursion
Problem: Given a telephone number print or produce all the possible telephone words or combinations of letters that can represent the given telephone number.
Solution: O(3 ^ n) (approximately - since there are 2 digits that have 4 letters)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] phoneNumber = new int[]{2,3,4};
List telephoneWords = GetTelephoneWords(phoneNumber, 0);
}
//get all the combinations / telephone words for a given telephone number
static List GetTelephoneWords(int[] numbers, int index)
{
List newWords = new List();
if (index == numbers.Length - 1)
{
newWords.AddRange(GetLetters(numbers[index]));
}
else
{
List wordsSoFar = GetTelephoneWords(numbers, index + 1);
string[] letters = GetLetters(numbers[index]);
foreach (string letter in letters)
{
foreach (string oldWord in wordsSoFar)
{
newWords.Add(letter + oldWord);
}
}
}
return newWords;
}
//gets the letters corresponding to a telephone digit
static string[] GetLetters(int i)
{
switch (i)
{
case 1: return new string[]{"1"};
case 2: return new string[] { "a", "b", "c" };
case 3: return new string[] { "d", "e", "f" };
case 4: return new string[] { "g", "h", "i" };
case 5: return new string[] { "j", "k", "l" };
case 6: return new string[] { "m", "n", "o" };
case 7: return new string[] { "p", "q", "r", "s" };
case 8: return new string[] { "t", "u", "v" };
case 9: return new string[] { "w", "x", "y", "z" };
case 0: return new string[]{"0"};
default: return new string[] { };
}
}
}
String: Combinations Using Recursion
Problem: Given a string of N characters, write a program to produce all combination of the characters. String "abc" should produce "a", "b", "c", "ab" , "ac", "bc", "abc".
Solution: The recursive solution proposed below runs in O(2 ^ n).
Pseudo Code:
1. If input string length = 1
return a list with the input string in it
2. if input string length > 1
a. Get list of combinations recursively for sub string without the
1st character
b. Prepend the 1st character to all the combinations received from step a. and
add to a new list of combinations;
c. Add all strings from step a. above
d. Add the 1st character to the new list of combinations
e. return this new list of combinations
Code (C#):
static List GetCombinations(string inputStr, int index)
{
List newCombinations = new List();
if (index == inputStr.Length - 1)
{
newCombinations.Add(inputStr.Substring(index));
}
else
{
List combinations = GetCombinations(inputStr, index + 1);
foreach (string str in combinations)
{
newCombinations.Add(str);
newCombinations.Add(inputStr[index].ToString() + str);
}
newCombinations.Add(inputStr[index].ToString());
}
return newCombinations;
}
String: Permutations Using Recursion
Problem: Write the code for producing/printing permutations of the characters in a string. For example: If "abc" is the input string, output permutations should be "abc", "bac", "bca", "acb", "cab", "cba".
Solution: There are at least 2 approaches to solving this problem. Even though both approaches use recursion, there is a subtle difference between the two. The second approach uses more number of recursive calls than the first and my rough analysis has shown that run time of both approaches is almost same. The first approach would be preferable given that the there are only n recursive calls compared to n! recursive calls of the second approach. Approach 1:
Pseudo Code:
Approach 2:
The idea here is to put each character in the string in the 1st position and combine it with the permutation of the characters in the rest of the string. As you can see this is also a recursive definition. Pseudo Code:
Solution: There are at least 2 approaches to solving this problem. Even though both approaches use recursion, there is a subtle difference between the two. The second approach uses more number of recursive calls than the first and my rough analysis has shown that run time of both approaches is almost same. The first approach would be preferable given that the there are only n recursive calls compared to n! recursive calls of the second approach. Approach 1:
Pseudo Code:
1. Set index = 0 to point to the 1st character in the input string
2. If index = n-1 return last character (n is length of input string)
3. Get Permutations of string starting at index + 1
4. For each permutation in the list from step 3
a. Insert input[index] character in all possible positions of each
permutation.
Example:
input = "abc"
get permutations for "bc": "bc" and "cb"
insert "a" in all positions of both "bc" and "cb":
"a" * "bc": "abc", "bac", "bca"
"a" * "cb": "acb", "cab", "cba"
Code (C#): List<string> Permute(string, str, int startIndex)
{
if(startIndex == str.Length -1 )
return new string[]{str.Substring(startIndex)};
List<string> permutations = Permute(str, ++startIndex);
List<string> newPermutations = new List<string>();
foreach(string permutation in permutations)
{
for(int i=0; i<permutation.Length; i++)
{
newPermutations.Add(permutation.Insert(i, str[startIndex]));
}
}
return newPermutations;
}
Analysis: Number of recursive calls is equal to N (length of the input string). if L is the level of each recursive call, the run time for each recursive call is L!. So at the top most call, since L = N, it is N!. Total: N! + N-1! + N-2! ... + 1 Approach 2:
The idea here is to put each character in the string in the 1st position and combine it with the permutation of the characters in the rest of the string. As you can see this is also a recursive definition. Pseudo Code:
For i=0 to N 1. Swap letters 0 and i. 2. Permute letters 1 to N-1, printing or saving the entire string each time.Code (C):
Permute(char* inputStart, char* current)
{
char *swap;
char temp;
if(*(current + 1) = '\0')
printf("%s\n", inputStart);
else
{
for(swap = current; *swap != '\0'; ++swap)
{
temp = *swap;
*swap = *current;
*current = temp;
Permute(inputStart, current + 1);
//revert the letters
*current = *swap;
*swap = temp;
}
}
}
Run time: This solution makes at least N! + N-1! + N-2!+ ... + 1 recursive calls doing 1 unit of work in each call. Compare this to the less number of recursive calls from the approach one, but approach one does increasing more work going back up from each recursive call.
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Convert Integer to String itoa
// val: integer that needs to be converted to string representation
// destBuffer: buffer where the output string will be written
// radix: is the radix of the numbering system (10 for decimal, 16 for Hexadecimal,
// 2 for binary)
char * my_itoa(int val, char * destBuffer, int radix)
{
if(val == 0)
{
destBuffer = "0";
return destBuffer;
}
bool isNeg = false;
// if input integer is negative set the isNeg flag and make it positive
// we will do the conversion using the absolute value and then append the
// the - sign in the end
if(val < 0)
{
isNeg = true;
val *= -1;
}
char *currentDest = destBuffer;
while(val > 0)
{
int digit = val % radix;
val /= radix;
*currentDest = (char) (digit + '0');
currentDest++;
}
if(isNeg)
{
*currentDest = '-';
currentDest++;
}
*currentDest = '\0';
reverse(destBuffer);
return destBuffer;
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Convert String To Integer atoi
Problem: Implement atoi function in C language and give the test cases. atoi function converts a string to an integer.
The function prototype is as follows:
ASCII value of a numeric character - ASCII value of the character '0' = int value of numeric character.
Ex: '8' - '0' = 8
Code:
int my_atoi(const char str[]);Solution: The key is to be able to find out the int value of a numeric character.
ASCII value of a numeric character - ASCII value of the character '0' = int value of numeric character.
Ex: '8' - '0' = 8
Code:
#define MIN_INT -2147483648
#define MAX_INT 2147483647
int my_atoi(const char str[])
{
if(str == NULL) return 0;
int len = strlen(str);
if(len <= 0) return 0;
int index = 0;
//skip leading spaces
while(str[index] == ' ') index++;
bool isNeg = str[index] == '-';
int outNum = 0;
if(isNeg)
{
index++;
// skip white space after the sign
while(str[index] == ' ') index++;
}
while(index < len)
{
char currentChar = str[index++];
if(currentChar >= '0' && currentChar <= '9')
{
int oldValue = outNum;
int charVal = currentChar - '0';
outNum *= 10;
outNum += charVal;
//overflow underflow detection
if(outNum < oldValue)
{
if(isNeg)
outNum = MIN_INT;
else
outNum = MAX_INT;
return outNum;
}
}
else
break;
}
if(isNeg)
outNum = outNum * -1;
return outNum;
}
atoi Test Cases:
Input : Output "" : 0 "0" : 0 "1" : 1 "-1" : -1 "10" : 10 "-10" : -10 "1234567890" : 1234567890 "23 45" : 23 " 99" : 99 " -66" : -66 "- 77" : -77 "55 " : 55 "-2147483648" : -2147483648 (MIN) "2147483647" : 2147483647 (MAX) "2147483648" : 2147483647 (overflow) "-2147483649" : -2147483648 (underflow) "abc*" : 0 "23ab" : 23 "23ab34" : 23 "b31" : 0
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Remove Specified Characters
Problem: You are given 2 strings. The first string is the input string that needs to be cleaned (in place) and the second string contains characters that need to be removed from the the first string. For example if string1 = "teetotaller" and removeString= "ae" then the output (cleaned string) will look like "ttotllr".
Solution:
The naive approach is as follows:
Improvement 1: The check to see if a character exists in the removeStr is O(m) where m is the size of the remove string. Hence the run time for loop from step 2 above is O(n * m).
If the check is somehow made to perform in O(1), the run time would be O(n). O(1) lookup can be done using a Hashtable or a flag array. Both techniques are compared in the Find First NonRepeated Character post. In this solution we'll use the array approach. We will assume that the character set is 7 bit ASCII, which means that there are 128 possible characters. The array of bools will be used to determine if a character is to be removed or not. The ASCII code value of the character itself will be used as an index in to the array. For example if 'a' is one of the characters in the remove string then removeArray['a'] will be set to true (removeArray['a'] = true;).
Improvement 2: The above proposed solution uses an output buffer to write the clean output characters to and then copies the output back to the original string. We don't really need the second buffer, if we just copy the characters to the input string instead of the output buffer. We will need to maintain a destination index to mark the spot where the next clean character needs to go. This improvement removes the need for the extra memory needed by the output buffer and also the need to copy it back to the original string.
With the help of above two improvements the run time is O(n). We now need extra memory for the array but its constant (not tied to n).
Improved Solution:
Solution:
The naive approach is as follows:
- Create an output buffer the same size of string1.
- Loop through individual characters of string1 and check if they exist in the removeString.
- Copy a character to the output buffer only if it doesn't exist in removeString.
- Copy the contents of the output buffer to string1.
Improvement 1: The check to see if a character exists in the removeStr is O(m) where m is the size of the remove string. Hence the run time for loop from step 2 above is O(n * m).
If the check is somehow made to perform in O(1), the run time would be O(n). O(1) lookup can be done using a Hashtable or a flag array. Both techniques are compared in the Find First NonRepeated Character post. In this solution we'll use the array approach. We will assume that the character set is 7 bit ASCII, which means that there are 128 possible characters. The array of bools will be used to determine if a character is to be removed or not. The ASCII code value of the character itself will be used as an index in to the array. For example if 'a' is one of the characters in the remove string then removeArray['a'] will be set to true (removeArray['a'] = true;).
Improvement 2: The above proposed solution uses an output buffer to write the clean output characters to and then copies the output back to the original string. We don't really need the second buffer, if we just copy the characters to the input string instead of the output buffer. We will need to maintain a destination index to mark the spot where the next clean character needs to go. This improvement removes the need for the extra memory needed by the output buffer and also the need to copy it back to the original string.
With the help of above two improvements the run time is O(n). We now need extra memory for the array but its constant (not tied to n).
Improved Solution:
- Loop through individual characters of string1 and check if they exist in the removeString.
- Copy a character back to the input string only if it doesn't exist in removeString.
- Terminate the string with a NULLCHAR ('\0').
//Removes the specified characters from an input string
void RemoveCharacters(char str[], char remove[])
{
int strLen = strlen(str);
int removeStrLen = strlen(remove);
bool removeCharacterFlags[128] = {false}; // assume ASCII character set
// set the flag for characters present in the remove string
for(int i=0; i<removeStrLen; i++)
{
removeCharacterFlags[remove[i]] = true;
}
int destIndex = 0; // index within the input string where the next
// clean character will go.
for(int i=0; i<strLen; i++)
{
if(!removeCharacterFlags[str[i]])
{
str[destIndex++] = str[i];
}
}
str[destIndex] = '\0';
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Find First Non-Repeated Character
Problem: Find the 1st non-repeated character in a string. Example: teetotaller
The 1st non-repeated character is o.
Solution: The solution involves keeping track of what characters in the string have a count of more than one. The choice of data structure we will use depends on the type of string. If the string is an ASCII string with 256 possible values then an array of size 256 would be sufficient to track the count of each character. But, if the string is a Unicode string with 65536 possible character values and the input string was a small string (few characters wide), using an array would be inefficient . In the case where our input string is relatively small and the character set is large we can use a HashTable instead. If the loading factor of the Hashtable was selected to be high (to save memory) it could potentially suffer from collisions, but since out string is small the chances of collisions are less. On the other hand if the string was a long string and the character set was small the array based solution would be more efficient memory wise.
Solution: The solution involves keeping track of what characters in the string have a count of more than one. The choice of data structure we will use depends on the type of string. If the string is an ASCII string with 256 possible values then an array of size 256 would be sufficient to track the count of each character. But, if the string is a Unicode string with 65536 possible character values and the input string was a small string (few characters wide), using an array would be inefficient . In the case where our input string is relatively small and the character set is large we can use a HashTable instead. If the loading factor of the Hashtable was selected to be high (to save memory) it could potentially suffer from collisions, but since out string is small the chances of collisions are less. On the other hand if the string was a long string and the character set was small the array based solution would be more efficient memory wise.
// returns the index of the 1st non-repeated character in the input string
int Find_First_Non_Repeated_Char(string s)
{
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
// populate the hash table with count for each character in the string
for(int i=0; i<s.Length; i++)
{
if(ht.Contains(s[i]))
{
int count = (int) ht[s[i]]; //get the count for the character
ht[s[i]] = ++count;
}
else
{
ht[s[i]] = 1;
}
}
// now go through the hash table one character at a time and find the
// one that has a count of 1
for(int i=0; i< s.Length; i++)
{
if(ht.Contains(s[i]) && (int)ht[s[i]] == 1)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1; // the input does not contain non-repeated character
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
Tree: Find Lowest Common Ancestor
 Problem: Given a binary search tree and 2 values find the lowest common ancestor.
Problem: Given a binary search tree and 2 values find the lowest common ancestor.
Solution: Lets take a sample tree and see what finding the lowest ancestor means. The figure to the left shows the sample tree. To take an example, lets say the problem asked us to find the lowest common ancestor for nodes 10 and 14. Visually we can tell that node 12 is the lowest common ancestor. 15 is also a common ancestor but its not the lowest.
Since the tree is a binary search tree all the nodes to the right of any node within the tree have greater values that the node itself and all the nodes to the left have smaller values than the node. This property helps us in implementing the optimal solution to this problem. We start analyzing values at the root node and recursively arrive at a node where the two input values fall on different sides of the node. If they are on the same side of the node we recursively analyze the corresponding branch. For example, we start at 15 and see that 10 and 14 are both less than 15, so we choose the left branch and arrive at 12. Now, 10 is on the left of 12 and 14 is on the right. This is the node we are interested in. There is a non-recursive solution to this problem which basically uses the same idea, which I'll post soon.
Code:
Node * Find-Lowest-Common-Ancestor(Node *pRoot, int val1, int val2)
{
if(pRoot == NULL) return NULL;
// if both the values are less than the current node value
// the common ancestor must be to the left
if(val1 < pRoot->data && val2 < pRoot->data);
{
return Find-Lowest-Common-Ancestor(pRoot->left, val1, val2);
}
// if both the values are greater than the current node value
// the common ancestor must be to the right
else if(val1 > pRoot->data && val2 > pRoot->data)
{
return Find-Lowest-Common-Ancestor(pRoot->right, val1, val2);
}
else
{
return pRoot;
}
}
Labels:
Tree
Tree: PreOrder Traversal without Recursion
Problem: Write the code for pre-order traversal of a binary tree without recursion.
Solution: Most problems involving binary trees can be solved by using recursion. Recursion is inherent to trees. But, keep in mind that recursion has a memory overhead because of the additional stack space required for the recursive method calls. Sometime interviewers will ask to solve problems related to trees without using recursion. This can sometimes make the problem challenging. In this problem, even though we will not use recursion explicitly, we will use the Stack data structure that emulates what recursion does.
Code:
Note: This implementation, even though avoids recursion, does not take any less memory compared to the recursive method since we are using an external stack to emulate recursion.
Solution: Most problems involving binary trees can be solved by using recursion. Recursion is inherent to trees. But, keep in mind that recursion has a memory overhead because of the additional stack space required for the recursive method calls. Sometime interviewers will ask to solve problems related to trees without using recursion. This can sometimes make the problem challenging. In this problem, even though we will not use recursion explicitly, we will use the Stack data structure that emulates what recursion does.
Code:
typedef struct _node
{
int data;
struct _node * left;
struct _node * right;
} Node;
void Pre-Order-Traversal-Non-Recursive(Node * root)
{
Stack nodeStack;
nodeStack.Push(root);
// while stack is not empty
while(nodeStack.Count > 0)
{
Node * currentNode = nodeStack.Pop();
printf("%d\n", currentNode->data);
nodeStack.Push(currentNode->right);
nodeStack.Push(currentNode->left);
}
}
Note: This implementation, even though avoids recursion, does not take any less memory compared to the recursive method since we are using an external stack to emulate recursion.
Labels:
Tree
Tree: Traversal (PreOrder, InOrder, PostOrder)
Problem: What are the different ways of traversing a non-empty Tree?
Solution: Tree traversal can be divided into 2 major methods. First is Depth-First-Traversal and the second is Breadth-First-Traversal.
Depth-First-Traversal(DFT or DFS): The idea is to recursively keep visiting the nodes in the left branch. When all nodes are visited in the left branch, visit the right branch recursively and move backup. Think of each branch(left or right) as a sub-tree.
Breadth-First-Traversal(BFT or BFS): Here all the nodes at the same level are visited before visiting nodes at a lower level. See the post on Breadth First Tree Traversal for an implementation using a Queue.
There are 3 different ways of Depth-First-Traversal depending on when the root node is visited with respect to the children sub-trees.
1. Pre-Order Traversal: The root node is visited before visiting the children nodes/sub-trees.
Algorithm:
a. Visit root node
b. Recursively visit left sub-tree
c. Recursively visit right sub-tree
Code:
2. In-Order Traversal: The root node is visited before visiting the right sub-tree but after visiting the left sub-tree.
Algorithm:
a. Recursively visit left sub-tree
b. Visit root node
c. Recursively visit right sub-tree
Code:
3. Post-Order Traversal: The root node is visited after visiting the left sub-tree as well as the right sub-tree.
Algorithm:
a. Recursively visit left sub-tree
b. Recursively visit right sub-tree
c. Visit root node
Code:
Solution: Tree traversal can be divided into 2 major methods. First is Depth-First-Traversal and the second is Breadth-First-Traversal.
Depth-First-Traversal(DFT or DFS): The idea is to recursively keep visiting the nodes in the left branch. When all nodes are visited in the left branch, visit the right branch recursively and move backup. Think of each branch(left or right) as a sub-tree.
Breadth-First-Traversal(BFT or BFS): Here all the nodes at the same level are visited before visiting nodes at a lower level. See the post on Breadth First Tree Traversal for an implementation using a Queue.
There are 3 different ways of Depth-First-Traversal depending on when the root node is visited with respect to the children sub-trees.
1. Pre-Order Traversal: The root node is visited before visiting the children nodes/sub-trees.
Algorithm:
a. Visit root node
b. Recursively visit left sub-tree
c. Recursively visit right sub-tree
Code:
PreOrderTraversal(Node * node)
{
if(node == NULL)
return;
printf("%d", node->data);
PreOrderTraversal(node->left);
PreOrderTraversal(node->right);
}
2. In-Order Traversal: The root node is visited before visiting the right sub-tree but after visiting the left sub-tree.
Algorithm:
a. Recursively visit left sub-tree
b. Visit root node
c. Recursively visit right sub-tree
Code:
PreOrderTraversal(Node * node)
{
if(node == NULL)
return;
PreOrderTraversal(node->left);
printf("%d", node->data);
PreOrderTraversal(node->right);
}
3. Post-Order Traversal: The root node is visited after visiting the left sub-tree as well as the right sub-tree.
Algorithm:
a. Recursively visit left sub-tree
b. Recursively visit right sub-tree
c. Visit root node
Code:
PreOrderTraversal(Node * node)
{
if(node == NULL)
return;
PreOrderTraversal(node->left);
PreOrderTraversal(node->right);
printf("%d", node->data);
}
Labels:
Tree
Implement a Queue using two Stacks
Problem: Implement a queue using 2 stacks
Solution: The solution involves using one of the stacks as inbox stack. Incoming items are pushed onto this stack. The other stack is used as an outbox. When items need to be dequeued from the Queue and the outbox stack is empty, all the items from the inbox stack are popped and pushed on to the outbox stack. From there they can be popped until the outbox stack is empty. If the outbox is not empty then Dequeue operation is just a simple Pop() on the outbox stack.
The Enqueue and Dequeue methods for the Queue are as follows:
Solution: The solution involves using one of the stacks as inbox stack. Incoming items are pushed onto this stack. The other stack is used as an outbox. When items need to be dequeued from the Queue and the outbox stack is empty, all the items from the inbox stack are popped and pushed on to the outbox stack. From there they can be popped until the outbox stack is empty. If the outbox is not empty then Dequeue operation is just a simple Pop() on the outbox stack.
The Enqueue and Dequeue methods for the Queue are as follows:
void Enqueue(int item)
{
// all incoming items go on to the inboxStack
inboxStack.push(item);
}
int Dequeue()
{
//if the outbox stack has items in it just pop it from there and return
if(outboxStack.Count > 0)
{
return outboxStack.Pop();
}
else
{
// move all items from the inbox stack to the outbox stack
while(inboxStack.Count > 0)
{
outboxStack.Push(inboxStack.Pop());
}
if(outboxStack.Count > 0)
{
return outboxStack.Pop();
}
}
}
Labels:
Data Structures
Tree: Breadth First Search
Problem: Write code for doing a breadth first search in a Tree data structure.
Solution: Breadth first search inspects items one level at a time starting with the root node. This is unlike the Depth First Search where the nodes in the left most branch are visited until there are no more nodes and then backtracks.
The problem with implementing a breadth first search is that we have to remember the list of nodes at the same level before moving to the next level. This can be achieved by using a queue data structure. See this post on details of how to implement a Queue using an array. Every time we visit a node, we inspect the data contained in the node before Enqueueing both children to the Queue. If the node contains the data we were searching for we return the pointer to that node.
Solution: Breadth first search inspects items one level at a time starting with the root node. This is unlike the Depth First Search where the nodes in the left most branch are visited until there are no more nodes and then backtracks.
The problem with implementing a breadth first search is that we have to remember the list of nodes at the same level before moving to the next level. This can be achieved by using a queue data structure. See this post on details of how to implement a Queue using an array. Every time we visit a node, we inspect the data contained in the node before Enqueueing both children to the Queue. If the node contains the data we were searching for we return the pointer to that node.
//Breadth First Search (BFS) method searches the tree one level at a time
Node * Breadth-First-Search(Node *root, int searchValue)
{
Queue queue;
queue.Enqueue(root);
Node * currentNode;
while(currentNode = queue.Dequeue())
{
if(currentNode->data == searchVal)
return currentNode;
queue.Enqueue(currentNode->left);
queue.Enqueue(currentNode->right);
}
}
Labels:
Data Structures,
Tree
Implement a Queue using an Array
Problem: Implement a queue using an Array. Make efficient use of the space in the array.
Solution: Queue is a data structure that supports Enqueue and Dequeue methods. The Enqueue method adds an item to the end of the list and Dequeue method removes an item from the beginning of the list. This means that the Queue is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure. Theoretically speaking a Queue doesn't have a fixed size. It grows as items are added to the end of the list. The implementation below has a fixed sized determined at the time of instantiating the Queue object. Ideally, the array should be reallocated to accommodate more items. The implementations makes use of the space efficiently by reusing space that is released when items are dequeued.
Solution: Queue is a data structure that supports Enqueue and Dequeue methods. The Enqueue method adds an item to the end of the list and Dequeue method removes an item from the beginning of the list. This means that the Queue is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure. Theoretically speaking a Queue doesn't have a fixed size. It grows as items are added to the end of the list. The implementation below has a fixed sized determined at the time of instantiating the Queue object. Ideally, the array should be reallocated to accommodate more items. The implementations makes use of the space efficiently by reusing space that is released when items are dequeued.
/************ Queue.h *********************/
// Queue class implements the Queue ADT(abstract data type) or Abstract Data Structure
// using an array as the underlying data structure
class Queue
{
private:
int *itemsArray; // array used for storing items in the queue
int startIndex; // index in the array where the queue starts
int size; // size of the array holding the queue
int count; // number of items in queue
public:
Queue(int size);
~Queue();
void Enqueue(int i);
int Dequeue();
int GetCount();
void Print();
};
/************ Queue.cpp *********************/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "malloc.h"
#include "Queue.h"
Queue::Queue(int size)
{
this->size = size;
itemsArray = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
startIndex = 0;
count = 0;
}
Queue::~Queue()
{
free(itemsArray);
}
// Enqueue method adds an item to the end of the queue
void Queue::Enqueue(int i)
{
if(count < size) // queue is not full
{
int destinationIndex = (startIndex + count) % size;
itemsArray[destinationIndex] = i;
count++;
}
else
{
printf("Queue is full...\n");
}
}
// Dequeue method removes an item from the front of the queue
int Queue::Dequeue()
{
if(count == 0)
{
printf("queue is empty!\n");
throw "queue is empty";
}
int ret = itemsArray[startIndex];
count--;
startIndex = (startIndex + 1)%size;
return ret;
}
int Queue::GetCount()
{
return count;
}
// Print the current contents of the queue
void Queue::Print()
{
printf("Queue contents: ");
for(int i = 0; i<count;i++)
{
printf("%d, ", itemsArray[(startIndex + i)%size]);
}
printf("\n");
}
Labels:
Data Structures
Interview Preparation Books
1. Programming Interviews Exposed
2. Programming Pearls
3. C#
4. ASP.NET
5. T-SQL Recipes
6. Operating Systems
7. Networking TCP/IP
8. Compilers
9. More Programming Pearls
10. Algorithms
11. Head First Patterns
12. Object Oriented Analysis and Design
13. Writing Secure Code
14. Code Complete
Microsoft Technical Phone Screen Interview Questions
General Questions
- What do you work on and what is your preferred area?
- What do you not like to work on?
Patterns & Design
- What patterns have you used?
- Whats a pattern that implements event driven programming model?
- When would you use inheritance vs encapsulation?
Xml Questions
- How do you validate an Xml document? Whats the difference between XSD and DTD?
- When do you use an Attribute vs an Element in an XML Schema?
- What are two major types of parsers? Which would you use?
SQL Questions
- Tradeoffs of indexing a table
- What is Denormalization? Why would you use it?
- INNER JOIN vs OUTER JOIN
Data Structures
- What underlying data structure would you use for implementing a Dictionary? Justify your choice?
How does the choice affect the runtime?
- What are different methods of resolving Hashtable collisions?
- Implement a Generic Stack Class in C#
C# Questions
- Explain delegates
- Whats the difference between delegates and events
- Explain lamda expressions and closure
- Asynchronous delegates. Whats does BeginInvoke and EndInvoke do?
Networking TCP/IP
- Compare and contrast TCP vs UDP. Give examples of applications that use each.
- How would you troubleshoot a connectivity issue with a computer?
Develeopment and Testing Practices
- How do you test your code?
- Do you write test cases before you write code? If yes, why?
- Do you do code coverage analysis? What are the code coverage numbers?
- What would you like those numbers to be? Can you acheive 100% coverage?
- What code analysis tools do you use? Whats the problem with using FxCop on ASP.Net code?
String: Palindrome Check
Problem: Find if a given string is a palindrome. Palindrome is a word or a phrase that reads the same in either direction.
Ex: A man, a plan, a canal, panama!
Punctuation and spaces can be ignored.
Solution: The solution is pretty straight forward and involves comparing the characters at both ends, incrementally moving towards the center of the string. This is similar logic we used for reversing a string in place. The IsPalindrome method implemented below assumes that the string has been cleaned off of the punctuation characters and spaces.
Code:
Ex: A man, a plan, a canal, panama!
Punctuation and spaces can be ignored.
Solution: The solution is pretty straight forward and involves comparing the characters at both ends, incrementally moving towards the center of the string. This is similar logic we used for reversing a string in place. The IsPalindrome method implemented below assumes that the string has been cleaned off of the punctuation characters and spaces.
Code:
bool IsPalindrome(char str[])
{
int len = strlen(str);
for(int i=0, j=len-1; i<j; i++, j--)
{
if(str[i] != str[j])
return false;
}
return true;
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Reverse Words
Problem: Reverse the words in a sentence. For example "Hello World" should become "World Hello".
Comment: This is one of most frequently asked interview questions on string manipulation.
Solution: First we reverse the entire string and then reverse each word of this reversed string.
Solution: First we reverse the entire string and then reverse each word of this reversed string.
"Hello World"
|
reverse
|
v
"dlroW olleH"
| |
reverse reverse
| |
v v
"World Hello"
Code:
void reverse(char str[], int beginIndex, int endIndex)
{
while(beginIndex < endIndex) // keep swaping characters as long as
// begin index is less than end index
{
// swap the characters
char temp = str[beginIndex];
str[beginIndex] = str[endIndex];
str[endIndex] = temp;
beginIndex++; //increment the begin index
endIndex--; //decrememnt the end index
}
}
void reverse_words(char str[])
{
reverse(str, 0, strlen(str)-1);
int currentIndex = 0;
int wordBeginIndex = 0;
int wordEndIndex = -1;
while(str[currentIndex])
{
if(str[currentIndex + 1] == ' ' // if we are at the word
|| str[currentIndex + 1] == '\0') // boundary or end of the string
{
wordEndIndex = currentIndex;
reverse(str, wordBeginIndex, wordEndIndex);
wordBeginIndex = currentIndex + 2;
}
currentIndex++;
}
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
String: Reverse in place
Problem: Given a string of unknown length reverse it in place.
Solution: Lets take a sample string "hello". When reversed it should read as "olleh". For those who are new to C/C++, a string has null terminator at the end. This null terminator denotes the end of the string. So, when you say declare a string in C language like: char *str = "hello"; If you notice, we just need to swap the first and the last characters, the 2nd and the 2nd last, 3rd and 3rd last and so on.
If you notice, we just need to swap the first and the last characters, the 2nd and the 2nd last, 3rd and 3rd last and so on.
Code:
Solution: Lets take a sample string "hello". When reversed it should read as "olleh". For those who are new to C/C++, a string has null terminator at the end. This null terminator denotes the end of the string. So, when you say declare a string in C language like: char *str = "hello";
How many bytes of memory does it take to store that string? 5 (for the characters) +1 (for the null). The representation of the string in memory looks like this:
Now, the reverse string should look like as shown below:

 If you notice, we just need to swap the first and the last characters, the 2nd and the 2nd last, 3rd and 3rd last and so on.
If you notice, we just need to swap the first and the last characters, the 2nd and the 2nd last, 3rd and 3rd last and so on.
Code:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char str[7] = "hello"; // create an array of characters of size 7
// and assign the string hello to it.
// Last char will be '\0' (null terminator)
printf("%s", str); // this will print hello
reverse(str);
printf("%s", str); // this will print olleh
return 0;
}
void reverse(char * str)
{
char * begin = str;
char * end = str;
// position the end pointer at the last character
while(*(end+1) != NULL)
{
end++;
}
while(begin < end) // as long as begin pointer is less than end pointer
{
// swap the characters
char temp = *begin;
*begin = *end;
*end = temp;
begin++; //increment the begin ptr
end--; //decrememnt the end pointer
}
}
Labels:
String Manipulation
Linked List Loop/Cycle Detection
Problem: Given the head pointer to a singly linked list with a loop or cycle in it. If you were to walk this list you never arrive at the end or the tail of the linked list. Find whether the list contains a loop in O(n) time and space complexity.
Observation: A linked list with a loop will have a node that is being pointed from 2 different node.
Solution 1: This problem was solved in the late 1960s by Robert W. Floyd. The solution is aptly named as Floyd's cycle finding algorithm a.k.a the Tortoise and Hare algorithm. It uses 2 pointers moving at different speeds to walk the linked list. Once they enter the loop they are expected to meet, which denotes that there is a loop. This works because the only way a faster moving pointer would point to the same location as a slower moving pointer is if somehow the entire list or a part of it is circular. Think of a tortoise and a hare running on a track. The faster running hare will catch up with the tortoise if they are running on circular track instead of a straight strip.
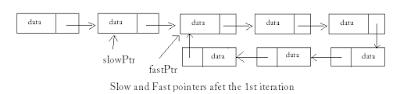 Code:
//returns true if the linked list contains a loop
Code:
//returns true if the linked list contains a loop
 Code:
//returns true if the linked list contains a loop
Code:
//returns true if the linked list contains a loop
bool ListContainsLoop(Node * head)
{
Node * slowPtr = head;
Node * fastPtr = head;
while(slowPtr && fastPtr)
{
fastPtr = fastPtr->next; // advance the fast pointer
if(fastPtr == slowPtr) // and check if its equal to the slow pointer
return true; // loop detected
if(fastPtr == NULL)
{
return false; // since fastPtr is NULL we reached the tail
}
fastPtr = fastPtr->next; //advance and check again
if(fastPtr == slowPtr)
return true;
slowPtr = slowPtr-next; // advance the slow pointer only once
}
return false; // we reach here if we reach the tail
}
Links
http://www.tekpool.com/
http://maxnoy.com/interviews.html
http://www.sellsbrothers.com/fun/msiview/default.aspx?content=question.htm
http://www.geekinterview.com/Interview-Questions/Programming
http://halcyon.usc.edu/~kiran/msqs.html
http://www.softwareinterview.com/
http://savenseek.com/page/Microsoft_Google_Algorithm_Interview_Questions__brainDead
http://savenseek.com/page/Amazon_Interview_Questions_Puzzles_and_Algorithms__geekygirl20
http://www.oliyiptong.com/blog/2006/05/30/amazon-sde-in-person-interview/
http://badsam.blogspot.com/2008/02/amazon-interview.html
Linked List: Merged List Problem
Problem: There are 2 singly linked lists (list1 and list2) that merge at one of the nodes and share the nodes there onwards. The goal is to find the node where these linked lists merge or join.
- Find length of both linked lists, say len1 and len2.
- Make current pointers for both lists equidistant from the common node. If one of the lists is longer we need to advance its current pointer by len1 - len2 (assuming list1 is longer). Now both current pointers should be equidistant from the common node. If both lists are same len, do nothing in step 2.
- Traverse both lists simultaneously while comparing the current pointers for equality. At ant point if they are equal we have found the first common node. If we reach the end of the lists without find the common node then the lists do not overlap.
Solution 2 : This solution only tells if the lists are joined, not where though. Interesting technique nevertheless.
- Update the tail of one of the lists to point to the head of the other.
- Now use the linked list cycle/loop detection technique to find if there is a loop in the combined list.
- If there is a loop then the list have node(s) in common, otherwise they don't.
Labels:
Linked List,
Microsoft,
MySpace
Linked List: Reverse
Question: Given the head pointer to a singly linked list reverse the list.
Solution 1: Recursive Approach - We can recursively traverse the linked list till we arrive at the last but one node. We then set the next pointer of the last node to point to the current node. We keep reversing the links as we unwind the recursive calls.
Code:
Solution 2: We can also reverse the singly linked list using an iterative approach. For some this approach can be easier to understand. Basically, we maintain 3 pointers (prevNode, currentNode, and nextNode). At each step we save the next of the currentNode in the nextNode ptr and reverse the link. After this, we advance the previous and current pointers.
Code:
Solution 1: Recursive Approach - We can recursively traverse the linked list till we arrive at the last but one node. We then set the next pointer of the last node to point to the current node. We keep reversing the links as we unwind the recursive calls.
Code:
// Takes a pointer to the head node of a singly linked list
// and returns the new head pointer for the reversed list
Node * Reverse(Node * head)
{
Node *newHead = Recursive_Reverse(head);
head->next = NULL; // since the first node is the last node now
// we need to set it's next pointer to NULL
return newHead;
}
Node * Recursive_Reverse(Node * node)
{
Node *nextNode = node->next;
if(nextNode == NULL) // if the list has only one node
{ // we don't need to reverse it
return node;
}
if(nextNode->next == NULL) // if nextNode is the last node we terminate the recursion
{
nextNode->next = node; // reverse the link
return nextNode; // return the ptr to the last node
// this will become the new head pointer
}
Node *head = Reverse(node->next); //recursively call Reverse
nextNode->next = node; // reverse the link
return head;
}
Solution 2: We can also reverse the singly linked list using an iterative approach. For some this approach can be easier to understand. Basically, we maintain 3 pointers (prevNode, currentNode, and nextNode). At each step we save the next of the currentNode in the nextNode ptr and reverse the link. After this, we advance the previous and current pointers.
Code:
//Takes a pointer to the head of a linked list
//Returns the pointer to the new head (old tail) node
Node * Iterative_Reverse(Node *head)
{
Node *prevNode = NULL; //pointer to the previous node
Node *nextNode = NULL; //pointer to the next node
Node *currentNode = head; //pointer to the current node
while(currentNode)
{
nextNode = currentNode->next; //save the pointer to the next node
//otherwise we will lose it as we
// overwrite it in the next step
currentNode->next = prevNode; //reverse the link
prevNode = currentNode; //set the current node as the previous node
//for the next iteration
currentNode = nextNode; //advance the current pointer
}
return prevNode;
}
Labels:
Linked List,
Microsoft
Linked List: Delete Node
Question: You are given a pointer to a node in a singly linked list. The head pointer is not available. Your task is to delete the specified node.
Solution: Typically, deleting a node from a singly linked list requires us to have the pointer to the node before the node to be deleted. We need this previous pointer so we can set it's Next pointer to the node after the specified node to be deleted. In this problem since we do not have the head pointer, we cannot walk the list and get the previous pointer.
We need to start thinking about what information does a linked list node have. Typically it has one or more data variables and a Next pointer that points to the next node in the linked list. If we were to overwrite the data in the specified node to be deleted from the next node in the list and delete this next node instead of the specified node, we would have effectively deleted the node. Technically, we don't delete the specified node but delete the next node after we copy data from it.
Note: This approach does not work in the case where the specified node to be deleted is the last node in the linked list.
Code: typedef struct _node
Solution: Typically, deleting a node from a singly linked list requires us to have the pointer to the node before the node to be deleted. We need this previous pointer so we can set it's Next pointer to the node after the specified node to be deleted. In this problem since we do not have the head pointer, we cannot walk the list and get the previous pointer.
We need to start thinking about what information does a linked list node have. Typically it has one or more data variables and a Next pointer that points to the next node in the linked list. If we were to overwrite the data in the specified node to be deleted from the next node in the list and delete this next node instead of the specified node, we would have effectively deleted the node. Technically, we don't delete the specified node but delete the next node after we copy data from it.
Note: This approach does not work in the case where the specified node to be deleted is the last node in the linked list.
Code: typedef struct _node
{
int i;
struct _node *next;
} Node;
void DeleteNode(Node *deleteThisNode)
{
if(deleteThisNode->next != null) //only if the specified node is not the last node of the list
// this approach does not work in that case
{
deleteThisNode->i = deleteThisNode->next->i; //copy data from the next node
Node * freeThis = deleteThisNode->next; //save the ptr to the next node, so we can free it
deleteThisNode->next = deleteThisNode->next->next; //point the Next pointer to the node after deleteThisNode->next
free(freeThis); //don't forget to free memory
}
}
Labels:
Linked List,
Microsoft
Linked List: Find the middle element
Question: Given a singly linked list, find the node in the middle.
Solution 1: Walk the linked list to find the length of the list. Lets say n is the length of the list. Walk the list again upto ⌊ n/2 ⌋.
Solution 2: Use two pointers. Move one pointer at twice the speed of the second. When the 1st pointer reaches the end of the list, the 2nd pointer will be pointing to the middle node. Note: If the list has even number of nodes, the middle node will be floor of ⌊ n/2 ⌋.
Code:
Solution 1: Walk the linked list to find the length of the list. Lets say n is the length of the list. Walk the list again upto ⌊ n/2 ⌋.
Solution 2: Use two pointers. Move one pointer at twice the speed of the second. When the 1st pointer reaches the end of the list, the 2nd pointer will be pointing to the middle node. Note: If the list has even number of nodes, the middle node will be floor of ⌊ n/2 ⌋.
Code:
Node * FindMiddle(Node *listHead)
{
Node *ptr1, *ptr2; // we need 2 pointers
ptr1 = ptr2 = listHead; // set the pointers to point to the list head initially
int i=0;
while(ptr1->next != NULL) // keep looping until we reach the tail
// (next will be NULL for the last node)
{
if(i == 0)
{
ptr1 = ptr1->next; //increment only the 1st pointer
i=1;
}
else if( i == 1)
{
ptr1 = ptr1->next; //increment both pointers
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
i = 0;
}
}
return ptr2; //now return the ptr2 which points to the middle node
}
Labels:
Linked List,
Microsoft
Linked List: Find n-th element from the tail
Question: Given a singly linked list find the n-th node from the back.
Solution 1: Reverse the linked list and select the n-th node from the head of the linked list.
Solution 2: Maintain 2 pointers n nodes apart. When the 1st pointer reaches the tail, the second pointer will be pointing to the desired node.
Notes: Both solutions take O(n) time but Solution 2 is more elegant.
Code:
Solution 1: Reverse the linked list and select the n-th node from the head of the linked list.
Solution 2: Maintain 2 pointers n nodes apart. When the 1st pointer reaches the tail, the second pointer will be pointing to the desired node.
Notes: Both solutions take O(n) time but Solution 2 is more elegant.
Code:
//define the list node
typedef struct _node
{
int i;
struct _node *next;
} Node;
Node * FindNthFromBack(Node *listHead, int n)
{
Node *ptr1, *ptr2; // we need 2 pointers
ptr1 = ptr2 = listHead; // set the pointers to point to the list head initially
while(ptr1->next != NULL) // keep looping until we reach the tail (next will be NULL for the last node)
{
if(n > 0)
{
ptr1 = ptr1->next; //increment only the 1st pointer
n--;
}
else
{
ptr1 = ptr1->next; //increment both pointers
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
}
}
return ptr2; //now return the ptr2 which points to the nth node from the tail
}
Labels:
Linked List,
Microsoft
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)